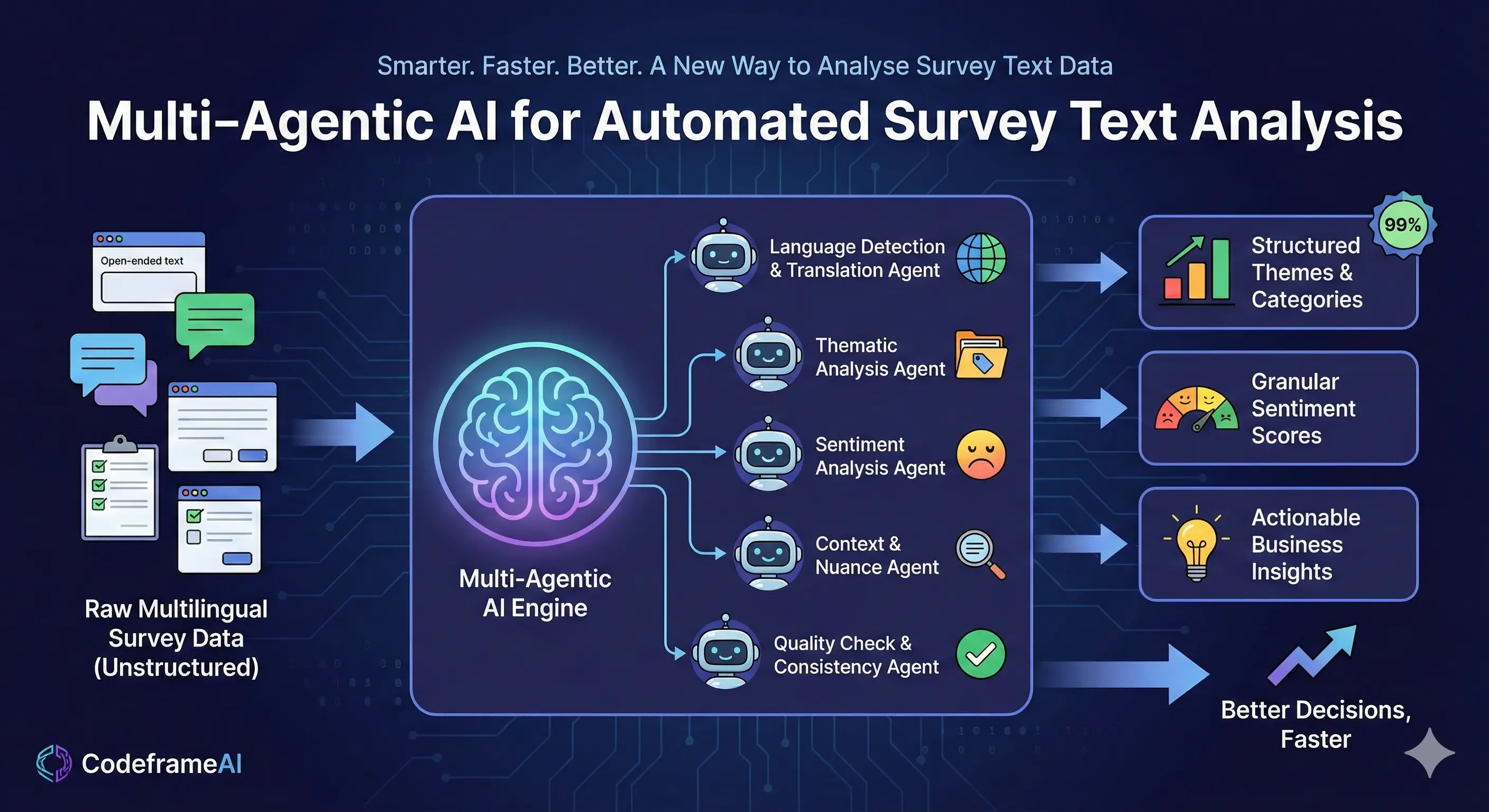
Smarter. Faster. Better. A New Way to Analyse Survey Text Data
Tired of tedious, costly, and inconsistent thematic and sentiment analysis for multilingual survey feedback? You’re not imagining the problem — it’s real, widespread, and growing fast.
Market surveys, employee feedback, customer reviews, social media comments, internal pulse surveys — organizations today are collecting more text data than ever before. This data is rich with insights, but extracting value from it often feels like an uphill battle. Whether the data arrives in batches or streams in real time, the core challenge remains the same: how do you analyse large volumes of unstructured text accurately, quickly, and consistently?
For decades, the answer was manual analysis. And that’s exactly where the problem begins.
The Hidden Cost of Manual Survey Text Analysis
Over the last 20 years and across thousands of projects, one pattern repeats itself again and again: teams struggle to keep up with the sheer volume of qualitative feedback.
Manual thematic and sentiment analysis is:
- Time-consuming: Requiring hours or days of reading and tagging.
- Expensive: Involving trained analysts and repeated review cycles.
- Inconsistent: Influenced by individual interpretation and fatigue.
- Hard to scale: Especially for large or multilingual datasets.
Two analysts can read the same response and code it differently. Multiply that inconsistency across thousands of responses, and insights become unreliable. The result? Decision-makers hesitate to trust the findings — or worse, act on incomplete information.
Why Traditional Automation Still Falls Short
Keyword-based tools and simple sentiment engines promised relief, but in practice, they often replicate the limitations of manual work. They may count words accurately, but they struggle to:
- Understand context and nuance.
- Handle mixed sentiment within a single response.
- Adapt when new themes emerge.
- Work effectively across multiple languages.
- Connect insights to real business actions.
So while analysis becomes slightly faster, it’s not necessarily smarter or more reliable. This is where a new approach changes the game.
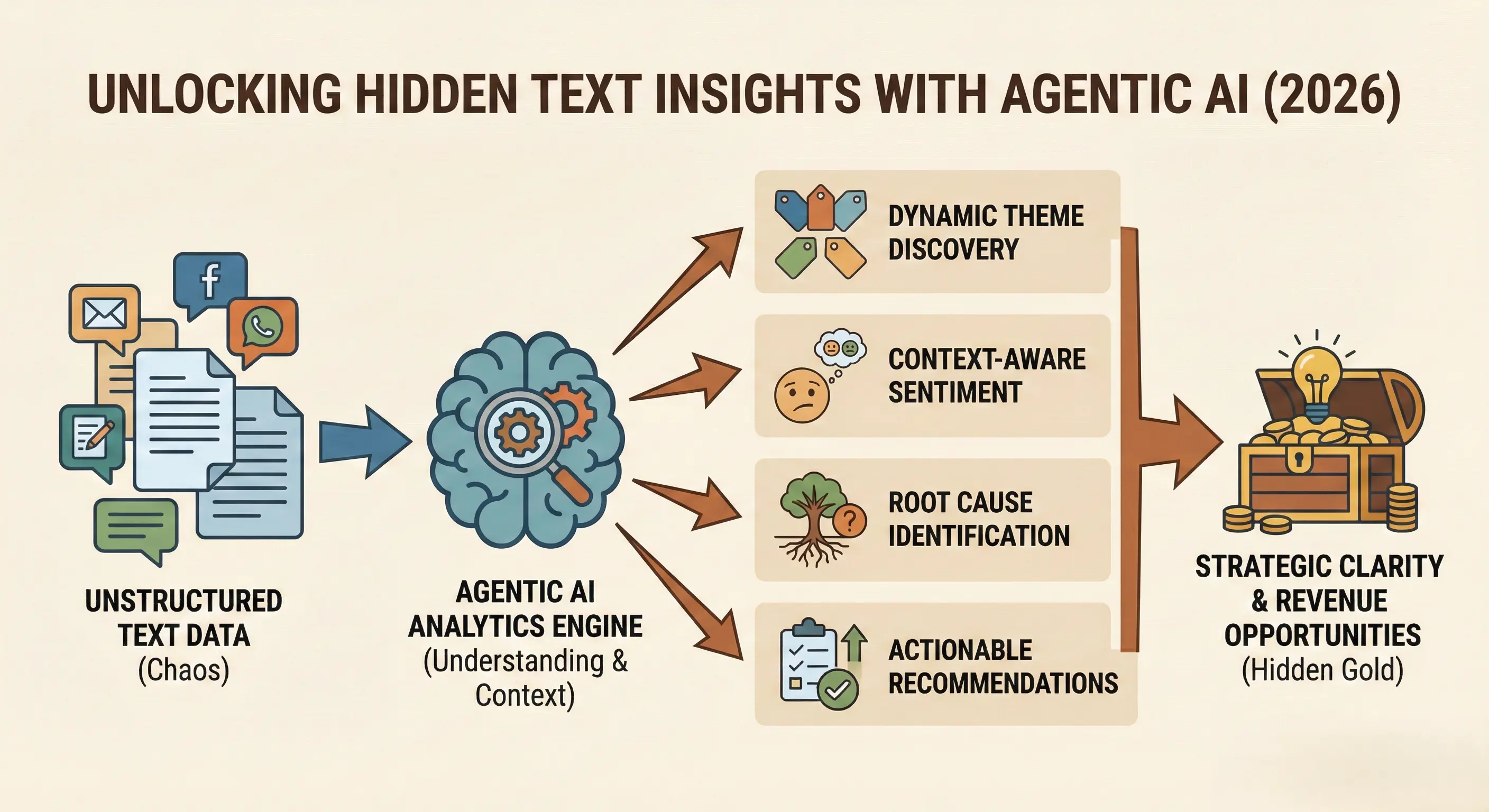
Multi-Agentic AI: A Smarter Way Forward
Multi-Agentic AI represents a fundamental shift in how survey text data is analysed. Instead of relying on a single static model, this approach uses multiple intelligent agents, each designed to perform a specific role — much like a team of expert analysts working together. One agent may focus on sentiment, another on theme discovery, another on language detection, and another on quality checks.
"Together, AI agents deliver results that are faster, more consistent, and more scalable than traditional methods."
What Makes This Approach Smarter?
1. Context-Driven Understanding
Multi-Agentic AI goes beyond keywords. It understands that phrases like “too complicated,” “hard to use,” and “confusing interface” often point to the same underlying usability issue — even when expressed differently.
2. Dynamic Theme Discovery
Instead of fixed codeframes, themes evolve automatically as new feedback patterns appear. This is critical when analysing real-time survey streams or social data.
3. Multilingual Intelligence
Feedback doesn’t stop at one language — and neither should analysis. Multi-Agentic systems can handle multiple languages seamlessly, ensuring consistent coding across regions without needing separate teams.
4. Built-In Consistency
Unlike humans, AI agents don’t get tired, rushed, or biased by prior responses. Every piece of text is analysed using the same logic, every time.
Faster, Cheaper, Better — by Design
Organizations adopting this smarter automated approach typically see dramatic improvements:
- Up to 70% cost reduction by minimizing manual effort.
- 10x–15x faster turnaround, even on large datasets.
- Consistent and auditable results, suitable for enterprise decision-making.
- Effortless scalability, from hundreds to millions of responses.
This isn’t about replacing analysts — it’s about freeing them from repetitive work so they can focus on interpretation, strategy, and action.
Who Benefits Most from AI Survey Analysis?
This approach is already transforming how multiple industries work with text data:
- Market Research Teams: Analyse verbatim responses at scale without sacrificing depth or accuracy.
- HR and People Analytics: Understand employee sentiment, engagement drivers, and emerging concerns from open-ended feedback.
- Customer Experience (CX) Teams: Identify recurring pain points and satisfaction drivers across surveys, chats, and reviews — before they impact loyalty.
- Corporate Managers and Consultants: Make faster, evidence-based decisions backed by reliable qualitative insights.
- Healthcare and Edu-Tech Professionals: Process sensitive, multilingual feedback efficiently while maintaining consistency and clarity.
Why This Matters Right Now
Text data is growing faster than any other form of business data. Customers expect personalized responses. Employees expect to be heard. Markets shift quickly. Organizations that still rely on slow, manual analysis risk:
- Missing early warning signals.
- Reacting too late to dissatisfaction.
- Making decisions based on partial insight.
Those that adopt smarter, AI-powered analysis gain clarity, speed, and confidence.
Final Thoughts
Survey text data is not a problem to manage — it’s an opportunity to unlock. But only if you analyse it the right way. A smarter, faster, and better approach using Multi-Agentic AI transforms verbatim analysis from a painful bottleneck into a strategic advantage.
If you’re ready to move beyond tedious, manual analysis, it’s time to explore a better way. Log in to learn how AI-powered innovation is reshaping survey text analysis — and giving teams back their time, confidence, and clarity.